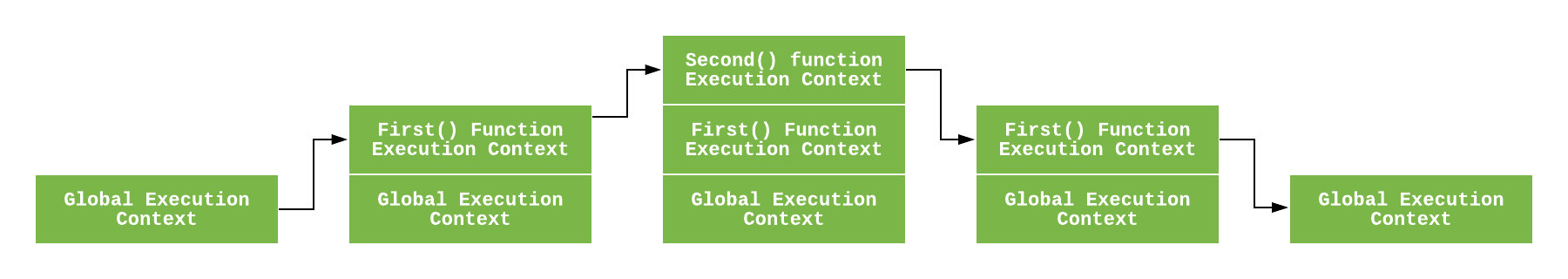
실행 컨테스트는 쉽게 말해 코드가 실행되고 있는 범위로 global, eval, function 만날 때 생성 된다. 각각의 실행 컨텍스트는 stack구조로 쌓이게 되고 마지막에 global code의 실행이 끝나면 프로그램이 종료된다.
Creation Phase
- LexicalEnvironment 컴포넌트 생성
- 변수와 해당 변수에 대입된 값이 매핑 됨
- Environmnet Records: Lexical environment 안에 함수와 변수를 기록한다.
- Declarative environment record: 변수와 함수 선언을 저장하는 곳이다.
- Object environment record: 전역 문맥과 with문에 나타나는 변수와 함수의 연관을 정의
-
Reference to the outer environment: 현재의 Lexical environment에서 변수를 찾지 못하면 외부 환경 참조
- This binding: this 값 결정
- Environmnet Records: Lexical environment 안에 함수와 변수를 기록한다.
- 변수와 해당 변수에 대입된 값이 매핑 됨
- VariableEnvironment 컴포넌트 생성
- Lexical Environment와 거의 비슷하다. 다만 Lexical에서는 함수 선언과 변수 let,const의 바인딩을 저장하고 Varialbe에서는 변수 var만 저장한다.
Execution Phase
Creation Phase에서 변수와 함수 선언 된것은 메모리에 저장된 상태(호이스팅)에서 자바스트립트 코드가 실행되는 때!
let a = 20;
const b = 30;
var c;
function multiply(e, f) {
var g = 20;
return e * f * g;
}
c = multiply(20, 30);
위의 코드가 실행되면,
GlobalExectionContext = {
LexicalEnvironment: {
EnvironmentRecord: {
Type: "Object",
// Identifier bindings go here
a: < uninitialized >,
b: < uninitialized >,
multiply: < func >
}
outer: <null>,
ThisBinding: <Global Object>
},
VariableEnvironment: {
EnvironmentRecord: {
Type: "Object",
// Identifier bindings go here
c: undefined,
}
outer: <null>,
ThisBinding: <Global Object>
}
}
글로벌 실행 컨텍스트가 실행되고, 위와 같이 Creation Phase때 만들어진 것들을 보게된다
GlobalExectionContext = {
LexicalEnvironment: {
EnvironmentRecord: {
Type: "Object",
// Identifier bindings go here
a: 20,
b: 30,
multiply: < func >
}
outer: <null>,
ThisBinding: <Global Object>
},
VariableEnvironment: {
EnvironmentRecord: {
Type: "Object",
// Identifier bindings go here
c: undefined,
}
outer: <null>,
ThisBinding: <Global Object>
}
}
코드 중 변수를 만나면 매핑 되어있는 변수에 값을 할당하고,
FunctionExectionContext = {
LexicalEnvironment: {
EnvironmentRecord: {
Type: "Declarative",
// Identifier bindings go here
Arguments: {0: 20, 1: 30, length: 2},
},
outer: <GlobalLexicalEnvironment>,
ThisBinding: <Global Object or undefined>,
},
VariableEnvironment: {
EnvironmentRecord: {
Type: "Declarative",
// Identifier bindings go here
g: undefined
},
outer: <GlobalLexicalEnvironment>,
ThisBinding: <Global Object or undefined>
}
}함수인 multiply(20, 30)를 만나면 새로운 실행 컨텍스트가 시작된다.
그렇게, 스택 구조로 반복
Resource
https://blog.bitsrc.io/understanding-execution-context-and-execution-stack-in-javascript-1c9ea8642dd0
https://meetup.toast.com/posts/129